cell
Size- and coating-dependent uptake of polymer-coated gold nanoparticles in primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells
[button href="http://doi.org/10.1021/bm300248u" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] Christian Freese, Matthew I. Gibso, Harm-Anton Klok, Ronald E. Unger, C. James Kirkpatrick
Interactions of silica nanoparticles with lung epithelial cells and the association to flotillins
[button href="http://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0876-5" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] Jennifer Kasper, Maria I. Hermanns, Christoph Bantz, Olga Koshkina, Thomas Lang, Michael
Uptake and cytotoxicity of citrate-coated gold nanospheres: Comparative studies on human endothelial and epithelial cells
[button href="http://doi.org/10.1186/1743-8977-9-23" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] Christian Freese, Chiara Uboldi, Matthew I Gibson, Ronald E Unger, Babette B Weksler, Ignacio
Natural Bactericidal Surfaces: Mechanical Rupture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cells by Cicada Wings
[button href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200528" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] Elena P. Ivanova, Jafar Hasan, Hayden K. Webb, Vi Khanh Truong, Gregory S. Watson, Jolanta
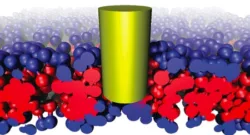
Translocation of nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes and polymers through bilayers
Cell membranes represent a serious protective barrier for external molecules, proteins, nanoparticles and drugs. This barrier is quite efficient in protecting the interior of the cells. However, large
Surface patterning of carbon nanotubes can enhance their penetration through a phospholipid bilayer
[button href="http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/nn102763b" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] [button
Can a carbon nanotube pierce through a phospholipid bilayer?
[button href="http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/nn1016549" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] [button href="http://arxiv.org/pdf/1010.1462v1" color="sea_foam" target="_blank"
Collision induced spatial organization of microtubules
[button href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2007.04.009" color="lime_green" target="_blank" id=""]PDF[/button] [button href="http://arxiv.org/pdf/cond-mat/0608717v1" color="sea_foam" target="_blank"